
Let’s be real: We welcome dogs into our homes and lives for the sweet, fun parts of pet parenthood — the tail wags and licks when we come home and all the nightly cuddles (even when these snuggle fests involve you losing a battle for blankets). Yet, caring for a dog also means being their healthcare proxy. Dogs of any age can develop issues, from fleas and allergies to diabetes and cancer.
Mange in dogs is another health condition to be mindful of — just in case. You may have seen severe mange on dogs in commercials raising awareness and funds for animal well-being, like for ASPCA. These pets have often been abused and neglected. However, mange in dogs can happen to beloved pets. Understanding signs of early-stage mange in dogs can help you get your pet prompt care. What does mange look like, and how is the condition treated? Good questions. Here’s what to know about dog mange.
What is mange in dogs?
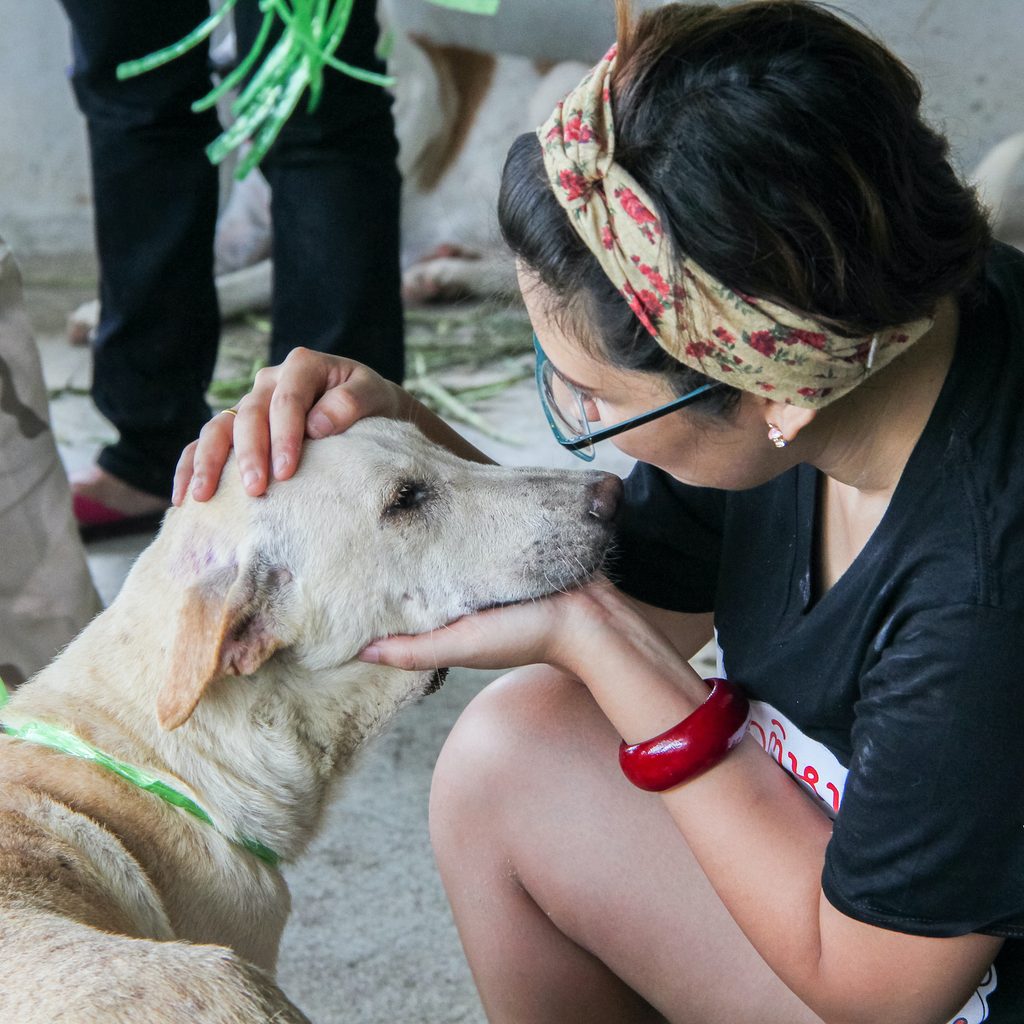

Dog mange is a skin disease. We’ll dig deeper into how dogs get mange in a bit. However, the short version is that certain kinds of mites can cause mange when they set up shop deep in a dog’s hair follicles. The two types of mange are:
- Sarcoptic mange. Commonly known as scabies, sarcoptic mange is more frequently found in dogs that have been abused and neglected. Shelters and rescue organizations may notice this mange on dogs living on the streets.
-
Demodectic mange. Demodex canis mites cause this type of mange. Perhaps surprisingly, Demodex canis is a typical part of a dog’s skin flora and is generally harmless. In fact, mother dogs pass them to their newborn puppies shortly after birth. These mites don’t spread to humans and are most dangerous in dogs with weaker immune systems, such as those with cancer or diabetes.
What does mange look like on a dog?
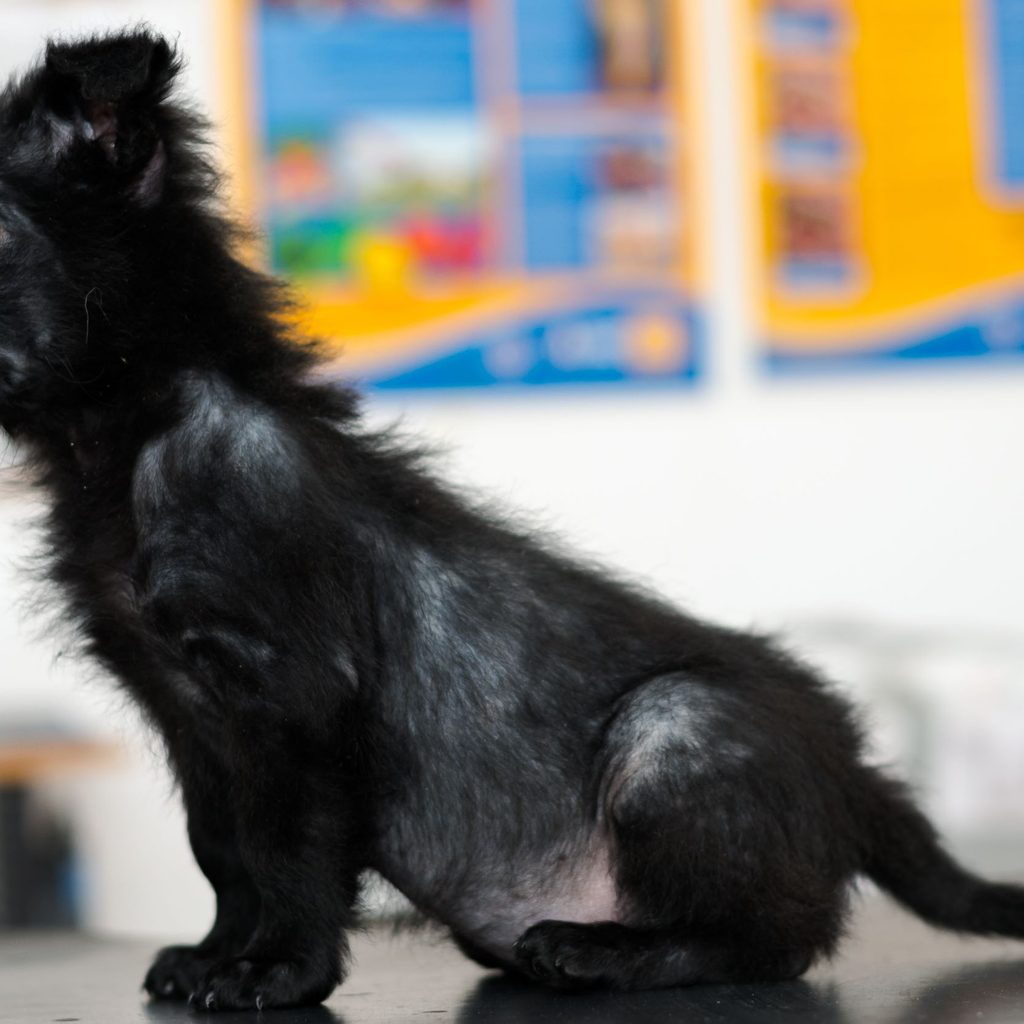

Clinical signs of mange in dogs include:
- Near constant itching
- Hair loss
- Wounds, potentially self-inflicted
- Raised bumps, especially on or around the chest
- Crusty skin, mainly around the ankle, armpit, elbow, or ear areas
Mange can also trigger other skin issues and side effects, such as:
- Skin infections
- Decreased energy
- Appetite loss
- Weight loss
- Depression
How do dogs get mange?

Mange is a skin disease caused by mites. The cause of a dog’s mange depends on the type the pup has. Demodectic mange is often passed from a mother to her puppies shortly after birth.
Sarcoptic mites can pass from dog to dog, especially if dogs share bedding or physically touch one another during play. Since sarcoptic mange is often associated with poor hygiene and neglectful conditions, you may feel guilty if your dog gets the disease — don’t. Sarcoptic mange is not always the result of infrequent bathing or neglect. Letting the disease fester can make symptoms more severe. Recognizing the flags and getting your dog quick care is a sign you are a great pet parent.
How do vets treat mange on dogs?
Since sarcoptic mange can spread from humans to dogs, you’ll want to handle your dog’s bedding and care with gloves. You’ll be instructed to wash anything they’ve touched, such as blankets and kennels. Unfortunately, you’ll also want to quarantine your dog away from you and other animals in the home until the condition clears up. Often, pups show improvement in the first two weeks, which is one reason it’s crucial to diagnose early-stage mange in dogs. Monthly or tri-monthly preventatives can help protect dogs from infections.
Since Demodectic mange doesn’t usually spread between humans or dogs, you probably won’t need to take the same cleaning measures. However, your dog will still take preventatives to ward off infection risk.
Regardless of the mange type, your pet will likely recover quickly. Severely immunocompromised dogs are the most at risk for poorer outcomes (as are ones that don’t get quick treatment).
A skin disease that comes from mite infestation causes mange in dogs. There are two types of mange. Demodectic is less severe and doesn’t require a full-house scrub down (usually), though preventatives can help ward off infection. Severely immunocompromised dogs are more at risk of becoming ill from Demodectic mange. Sarcoptic mange, or scabies, can be transmitted from dog to dog and human. Signs include severe itching, wounds (sometimes self-infected), and bumps on the skin. While poor hygiene often causes the disease, the mites can transmit during playtime between dogs or through bedding. Letting mange fester and go untreated can make the condition more severe (and uncomfortable). Your pet’s vet can prescribe the best treatment. Most pups will make a full recovery.



